【論文サーベイ】Survey on Pre-Trained Model-based Continual Learning
144 Views
January 13, 25
スライド概要
Web Developer / Research on generative models and continual learning
関連スライド
各ページのテキスト
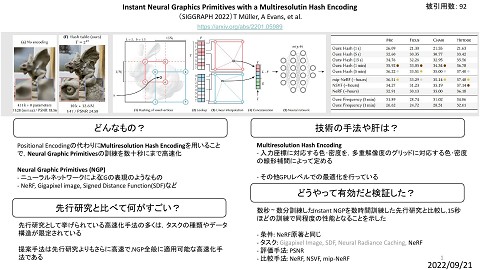
Survey on Pre-Trained Model-based Continual Learning Continual Learning with Pre-Trained Models: A Survey D. Zhou, Q. Wang, J. Ning, H. Ye, D. Zhan [IJCAI’24] 1
Background Continual Learning 1つのモデルで新しいタスクを段階的に学習していく設定 2
Background Pre-Trained Model-based Continual Learning (PTM-based CL) Pre-Trained Model を初期状態とした Continual Learning 3
Background Catastrophic Forgetting Continual Learning では Catastrophic Forgetting が最大の課題となる - 新しいタスクを学習すると,それ以前に学習したタスクを忘れてしまう現象 Continual Learningを続けると 著しく精度が下がる 4
PTM-based CLの研究分野 Prompt-Based Methods Model Mixture-Based Methods Representation-Based Methods ● L2P [2022] ● SimpleCIL [2023] ● ESN [2023] ● Dual-prompt [2022] ● APER [2023] ● LAE [2023] ● S-prompts [2022] ● RanPAC [2023] ● PromptFusion [2023] ● CODA-prompt [2023] ● LayUP [2023] ● PROOF [2023] ● DAP [2023] ● SLCA [2023] ● Hide-Prompt [2023] ● APG [2023] ● EASE [2024] ● ZSCL [2023] 5
Prompt-based Methods - PTMは強い 汎化性能 を持っている - PTMのモデル全体をチューニングすると,汎化性能 が上書きされてしまう - lightweight module のみをチューニングすることが重要 Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) で prompt のみをチューニングする手法が提案された 6
Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) M. Jia, L. Tang, B. Chen, C. Cardie, S. Belongie, B. Hariharan, S. Lim [ECCV’22] - 入力に学習可能なパラメータ (prompt) を追加し,head+prompt のみをチューニングする - 全体の1%ほどのパラメータにしかならない - 20 / 24 のタスクでフルファインチューニングを上回る精度 cls token prompt img embedding 7
Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) M. Jia, L. Tang, B. Chen, C. Cardie, S. Belongie, B. Hariharan, S. Lim [ECCV’22] ViT VPT-Shallow 8
Prompt Pool - VPT の中で prompt の集合 prompt pool を保持する - Input Instance に対して prompt pool から最適な prompt を選択する仕組みが重要 9
Learning to Prompt for Continual Learning (L2P) Z. Wang, Z. Zhang, C. Lee, H. Zhang, R. Sun, X. Ren, G. Su, V. Perot, J. Dy, T. Pfister [CVPR’22] - key-query matching によって 学習可能な key に prompt を割り当てる - key と 特徴ベクトル - top-N set から制約項を作る の cosine 距離 が小さい順に top-N set を作る 10
DualPrompt: Complementary Prompting for Rehearsal-free Continual Learning Z.Wang, Z. Zhang, et. al [ECCV’22] - prompt pool を タスク共通 G / タスク特化 E の prompt に分解する + - validation set を使って VPT-deep の深さを調整する G Prompt と E Prompt は 同じ層に入力されないようにする 11
CODA-Prompt: COntinual Decomposed Attention-based Prompting for Rehearsal-Free Continual Learning J. S. Smith, L. Karlinsky, et. al [CVPR’23] - prompt matching は難しい - prompt pool から1つの prompt を選択するのではなく 全ての prompt の重み付き和を Input Instance の prompt とする手法 - 重みの計算は attention vector を使う 12
Generating Instance-level Prompts for Rehearsal-free Continual Learning (DAP) D. Jung, D. Han, et. al [ICCV’23] - ViTの入力から prompt を生成するMLPを学習する手法 - 精度が非常に良いが,評価が怪しい 13
Representation-based Methods - PTM は既に下流タスクの情報を持っていると考える - adapter network や projector を使って PTMが持つ下流タスクの情報を強 調することが重要となる 14
Revisiting Class-Incremental Learning with Pre-Trained Models: Generalizability and Adaptivity are All You Need (SimpleCIL, APER) D. Zhou, H. Ye, D. Zhan, Z. Liu [ICLR’24 withdrawn] SimpleCIL - クラスごとの特徴ベクトル の平均 (prototype) を考える - prototype を fc層 として cosine classifier で分類する 15
Revisiting Class-Incremental Learning with Pre-Trained Models: Generalizability and Adaptivity are All You Need (SimpleCIL, APER) D. Zhou, H. Ye, D. Zhan, Z. Liu [ICLR’24 withdrawn] APER: AdaPt and mERge PTM for CIL - prompt や adapter のような省メモリな module を使って PTM をチューニングする - prototype は PTM と Adapted Model の特徴ベクトルを連結したものを使う 16
実験 (CIL) PTMには ImageNet21K でpre-trained な ViT (ViT-B/16-IN21K) を使用 全タスクの top-1 acc の平均 最終的な top-1 acc representation-based な手法が強い